Quality control is a cornerstone of the manufacturing industry. It ensures that products meet specific standards, satisfy customer expectations, and comply with regulations. Effective quality control not only enhances the reliability and reputation of a company but also optimizes operational efficiency, reduces costs, and mitigates risks. In this blog, we will delve into the importance of quality control in manufacturing, its key elements, benefits, and best practices for implementation.
What is Quality Control in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in manufacturing refers to the process of inspecting, testing, and monitoring products to ensure they meet predefined quality standards. It involves a series of activities aimed at identifying defects, inconsistencies, or deviations from the desired specifications at various stages of the production process. QC is a proactive approach that helps to detect and address issues before products reach the customer, thus preventing costly recalls and damage to the brand’s reputation.
The Role of Quality Control in Manufacturing
Quality control plays several critical roles in manufacturing, including:
- Ensuring Product Quality: The primary goal of quality control is to ensure that every product leaving the factory meets the required standards. This involves rigorous testing and inspection processes to identify any defects or deviations. High-quality products lead to customer satisfaction, repeat business, and positive reviews, which are essential for a company’s success.
- Compliance with Standards and Regulations: Manufacturing industries are subject to various regulations and standards, depending on the sector and location. Quality control ensures that products comply with these regulations, avoiding legal issues, fines, and sanctions. Compliance is particularly crucial in industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where safety and reliability are paramount.
- Reducing Costs: While implementing quality control processes involves an initial investment, it ultimately leads to cost savings. By identifying defects early in the production process, manufacturers can prevent the waste of materials, reduce rework, and avoid the costs associated with product recalls and customer returns. Efficient QC processes minimize the occurrence of defects, thereby optimizing resource utilization and reducing production costs.
- Building Brand Reputation: Consistently delivering high-quality products builds a strong brand reputation. Customers are more likely to trust and recommend brands that meet their expectations for quality. A solid reputation enhances brand loyalty, attracts new customers, and differentiates a company from its competitors. On the other hand, poor quality can lead to negative reviews, loss of business, and a damaged reputation.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Quality control streamlines manufacturing processes by identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. By continuously monitoring and analyzing production processes, manufacturers can optimize their operations, enhance productivity, and achieve higher levels of efficiency. Efficient QC processes contribute to smoother workflows, reduced downtime, and faster production cycles.
Key Elements of Quality Control in Manufacturing
To effectively implement quality control in manufacturing, it is essential to understand its key elements:
- Quality Standards and Specifications: Defining clear quality standards and specifications is the foundation of effective quality control. These standards outline the acceptable levels of quality for products, including dimensions, materials, performance, and safety requirements. Quality standards should be based on customer expectations, industry regulations, and company objectives.
- Inspection and Testing: Inspection and testing are core components of quality control. These activities involve examining products at various stages of production to identify defects or deviations from the set standards. Inspections can be visual, dimensional, or functional, depending on the nature of the product. Testing may involve physical tests, chemical analyses, or performance evaluations to ensure that products meet the required quality criteria.
- Process Control: Process control involves monitoring and controlling the manufacturing processes to maintain consistent product quality. This includes setting up control charts, monitoring key process parameters, and implementing corrective actions when deviations occur. Process control helps to identify and address issues in real-time, preventing defects and ensuring uniformity in production.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Collecting and analyzing data is crucial for effective quality control. Data provides insights into the performance of products and processes, enabling manufacturers to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques, such as control charts and capability analysis, are commonly used to analyze data and make informed decisions.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA): When defects or quality issues are identified, it is essential to implement corrective and preventive actions. Corrective actions address the root cause of the problem to prevent its recurrence, while preventive actions focus on eliminating potential issues before they occur. CAPA processes involve identifying the root cause, developing and implementing solutions, and monitoring the effectiveness of the actions taken.
- Training and Education: Quality control is a collective effort that requires the involvement of all employees. Providing training and education on quality standards, inspection techniques, and process control ensures that employees understand their roles in maintaining product quality. A well-trained workforce is more likely to identify and address quality issues effectively, contributing to a culture of continuous improvement.
Benefits of Quality Control in Manufacturing
Implementing quality control in manufacturing offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Product Quality: Quality control ensures that products meet the required standards, resulting in high-quality products that satisfy customer expectations. Consistent product quality enhances customer satisfaction, loyalty, and brand reputation.
- Reduced Waste and Rework: By identifying defects early in the production process, quality control reduces the need for rework and minimizes waste. This leads to more efficient use of materials, labor, and resources, resulting in cost savings and increased profitability.
- Lower Risk of Recalls: Quality control helps to prevent defective products from reaching the market, reducing the risk of product recalls. Recalls can be costly and damaging to a company’s reputation. Effective QC processes minimize the likelihood of recalls, protecting the brand and maintaining customer trust.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Quality control streamlines production processes by identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement. By optimizing processes, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of productivity, reduce downtime, and increase throughput. Efficient QC processes contribute to faster production cycles and shorter lead times.
- Compliance with Regulations: Quality control ensures that products comply with industry standards and regulations, avoiding legal issues, fines, and sanctions. Compliance is essential for maintaining market access and meeting customer requirements, particularly in regulated industries.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Quality control provides valuable data that can be used to make informed decisions. By analyzing data, manufacturers can identify trends, predict issues, and implement proactive measures to improve quality and efficiency. Data-driven decision-making enhances the overall effectiveness of quality control processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Quality control fosters a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging the identification and resolution of quality issues. By continuously monitoring and analyzing processes, manufacturers can implement changes that lead to ongoing enhancements in product quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Implementing Quality Control in Manufacturing
To achieve the benefits of quality control, manufacturers should adopt the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Quality Standards: Define clear and measurable quality standards that align with customer expectations, industry regulations, and company objectives. Communicate these standards to all employees and ensure that they are consistently applied throughout the production process.
- Implement a Robust Inspection and Testing Process: Develop a comprehensive inspection and testing process that covers all stages of production. Use a combination of visual inspections, functional tests, and statistical methods to identify defects and ensure product quality. Regularly review and update inspection and testing procedures to keep pace with changing requirements.
- Utilize Statistical Process Control (SPC): Implement SPC techniques to monitor and control manufacturing processes. Use control charts, capability analysis, and other SPC tools to identify trends, variations, and potential quality issues. SPC helps to maintain consistent product quality and optimize process performance.
- Invest in Training and Education: Provide ongoing training and education to employees on quality standards, inspection techniques, and process control. Encourage employees to take an active role in quality control and empower them to identify and address quality issues. A well-trained workforce is essential for effective quality control.
- Implement Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA): Develop a robust CAPA process to address quality issues and prevent their recurrence. When defects are identified, conduct a thorough root cause analysis, implement corrective actions, and monitor their effectiveness. Proactive CAPA processes help to prevent issues before they occur, enhancing overall product quality.
- Leverage Technology and Automation: Use technology and automation to enhance quality control processes. Automated inspection systems, sensors, and data analytics tools can improve accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in quality control. Embrace digital transformation to stay competitive and meet the evolving demands of the manufacturing industry.
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by promoting open communication, collaboration, and innovation. Engage employees in problem-solving and decision-making processes, and recognize their contributions to quality improvement. Continuous improvement leads to sustained excellence in product quality and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Quality control is a vital component of the manufacturing industry, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of quality, safety, and reliability. By implementing effective quality control processes, manufacturers can enhance product quality, reduce costs, comply with regulations, and build a strong brand reputation. The benefits of quality control extend beyond the production line, contributing to customer satisfaction, business success, and long-term sustainability. As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, investing in quality control is essential for staying competitive and achieving excellence in the industry.
Top 15 MNCs Every Mechanical Engineer Dreams of Joining in 2025
Mechanical engineering is one of the most diverse and essential fields in the world. Every…
How to Digitize and Automate the CAPA Process
In today’s competitive and fast-paced business environment, ensuring operational efficiency and maintaining high-quality standards are…
Top 10 Essential Tools Every Mechanical Engineer Should Know
Mechanical engineering revolves around precision, efficiency, and innovation. To achieve excellence in design and manufacturing,…
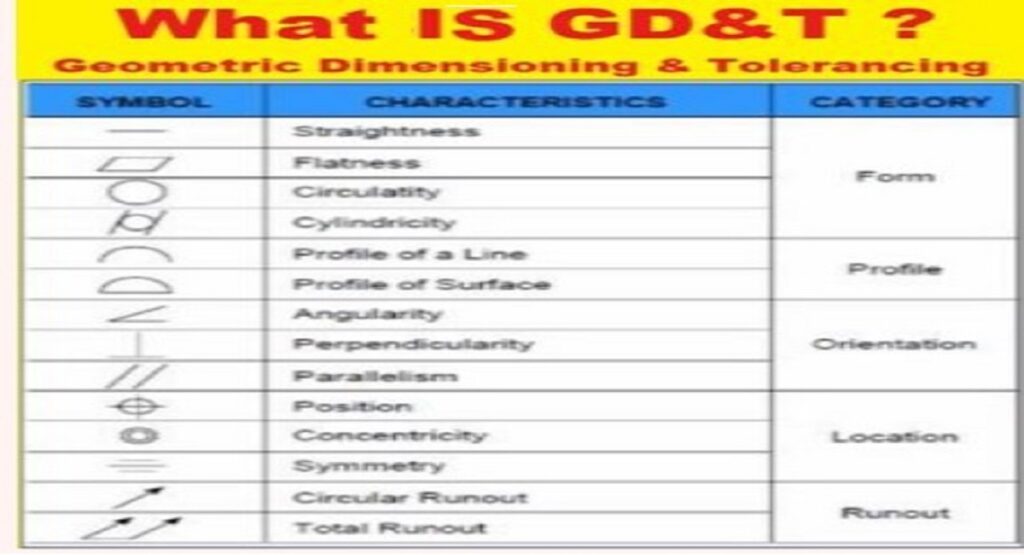
What is GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) ?
GD&T is an international language used to describe a part accurately. It comprises symbols, rules,…
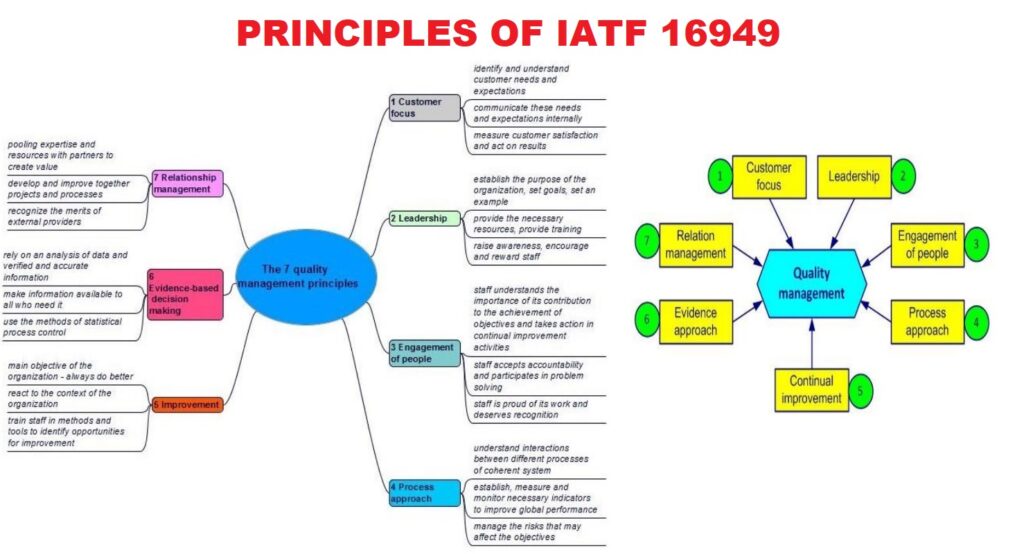
Principles of IATF 16949: A Guide to Quality Management
The Principles of IATF 16949 are essential for achieving excellence in the automotive industry. IATF…
The Evolution of IATF 16949: The Automotive Quality Standard
Introduction to IATF 16949 The IATF 16949 standard is a globally recognized certification for Quality…